At every IMTS, the newest and most impressive industrial robot technology is on display — from the massive (IMTS booths and arm that moves a full-sized sports car with ease, to the welding robots that make part assemblies all day, every day. The technology used in these robots is driving startups to develop personal assistant robots for people with limited mobility to live at home more independently. Here are two examples of those startups.
Retriever robot
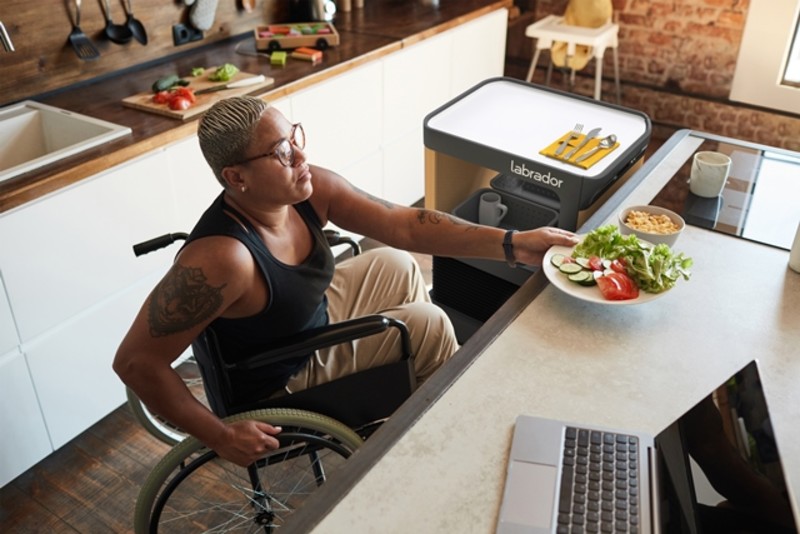
The Retriever is a mobile personal robot developed to improve quality of life for people whose daily physical activities are impacted by pain, injury, or other health issues. The Retriever looks somewhat like a standard utility cart, but is, in fact, a sophisticated robotic retrieval system to empower people to do everyday tasks, such as bring food or medication to the user from pre-loaded trays in the home. See the Retriever in action .
Industrial robot design is the basis for many aspects of the Labrador Retriever.
“The robot’s navigation stack uses the same core algorithms as those used for 3D virtual positioning in augmented reality applications,” says , CEO at Labrador. “What’s different is that we combine that with other software modules as well as customized hardware to track and move things in the real world. The result is that we can map the environment and create ‘bus stops’ where the robot should go, such as the refrigerator or beside a chair, and easily navigate from one place to the other in highly unstructured home environments.”
The systems run on an ROS (Robot Operating System) but on a very low-cost computer, where all the processing is done on the edge. To keep costs low, the Retriever uses components from mass-market consumer electronic devices, like cameras, GoPros, and other sensors found in mobile phones, instead of more expensive solutions such as an industrial LIDAR. The lower cost enables the Retriever to have redundant systems, such as pressure-sensitive surfaces that can detect if someone braces or leans on the robot while it’s driving.
A robot for mom
Dooley’s personal experience was his inspiration to start Labrador in 2017.
“My mom started using a cane and a walker when she was in her eighties, and I realized that she was using her hands as extra pair of legs to stabilize herself and move around the home,” Dooley says. “So tasks where she had to move other things while trying to move herself, such as setting the table or carrying a laundry basket, became very difficult and potentially even dangerous. The initial case for the Labrador robot was to be an extra pair of hands to help people move things to where they need to be.”
Dooley’s interest in robot innovation began in the late 1990’s when he helped launch , a line of robot building systems for kids that use LEGO bricks and electronic components. 10 years later, Dooley co-invented and helped launch one of the first “smart” robotic floor cleaners that could systemically map and track its position as it cleans.
By working on those projects, Dooley and other members of the team at Labrador learned a lot about the technical complexities of operating robots in home settings, as well as how to make things extremely simple and natural for people to use.
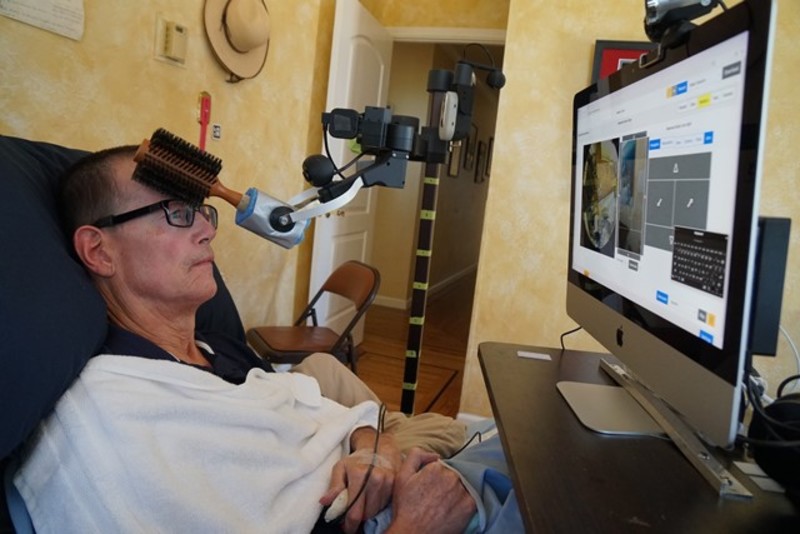


Henry Evans uses the Stretch mobile manipulator to brush his hair.
Mobile manipulator
is taking personal assistant robots to a new level by adding manipulation abilities. For people with limited mobility, the mobile manipulator acts like a physical surrogate while the operator controls it from one of several interface options (such as a gamepad or computer) to do everyday activities around the home, such as getting a beverage from the refrigerator or unloading laundry from the washing machine. Essentially, the Stretch looks like a Roomba with a telescoping robotic arm attached, but it is much more complex than it appears. Learn more about the latest Stretch developments .
Much like an industrial robot, Stretch features a gripper, a telescopic arm, multiple cameras, a computer, and sensors software. The Stretch comes with a calibrated robot model () that is well-aligned to 3D camera images and is ROS-compatible with user-friendly, open-source ROS-python libraries. It is pre-loaded with demo code for a number of autonomous capabilities, such as navigation, mapping, and manipulation.
Access for everyone
Hello Robot was founded in 2017 by , the director of robotics at Google, and , formerly a tenured professor who conducted robotics research at Georgia Institute of ��������ֱ��. Both were looking for a greater social impact and saw an opportunity to build off the research, so they started Hello Robot.
Development of the Stretch has been a true interdisciplinary endeavor, with the combined efforts of occupational therapists, speech language pathologists, human factors specialists, robotics engineers, and computer scientists.
�ċ�ċ�ċ�ċ��������ֱ�� + humanity
One contributor to the development of Stretch is , a robotic applications engineering intern. She was working on her biomedical engineering degree at the University of California-Davis when she discovered an interest in orthopedic biomechanics. Seeing the potential for robots to help people lead better lives, she continued her education and got a master’s degree in robotics from Northwestern University.
Garverick worked side-by-side with , an occupational therapy clinical research lead at Hello Robot, to develop the earliest version of Stretch. They conducted in-situ research by living with Henry Evans, who suffered a stroke and became quadriplegic. Evans is the co-founder of , an organization that supports the development of assistive robot technology for people with disabilities.
Gaverick and Nguyen observed Evans’ activities of everyday life to see how he interacted with the robot so they could refine the design. Evans controls his Stretch with a head-tracking device that turns his tiny head movements into cursor movements on the screen and uses a mouse to click on the web interface controls. With these computer clicks, he can use the web-based interface to direct the robot to help him do many everyday activities independently, such as eat, shave, and even pick a rose from a vase to give his wife — actions he had not been able to do for himself for decades. This summer he played with his granddaughter for the first time. The Stretch is in its third phase of research and is expected to be commercially available in two years.
Another use for robots in manufacturing
As assistive robot technology advances, there may be opportunities to adopt some of those functions in manufacturing robots to improve work conditions, reduce physical strain on workers, and even enable people with disabilities to work in manufacturing.
“If a wheelchair user worked in manufacturing, they could potentially use a robot to augment some of their work tasks, such as reaching down or reaching ahead to grab items,” Nguyen predicts. “For a person with significant motor impairments, the robot could be an extension for them to manipulate their environment in that workspace so they can continue their work.”
Robots of the future
Robots and their capabilities continue to expand in all aspects of life, from the workplace to the home — even to outer space! It will be exciting to see what new advanced robot technology and products will take the world by storm at IMTS 2024. The at is a new section of the show floor dedicated to all things automation and robotics, which promises to be abuzz with innovations we can only imagine today.
Register now at .